Edmond Halley planted this constellation in the southern sky in 1678 as a patriotic gesture to his monarch, Charles II of England. It commemorated the oak tree in which King Charles hid after his defeat by Oliver Cromwell’s republican forces at the Battle of Worcester in 1651. Halley formed the constellation from stars that were previously part of Argo Navis.
The invention arose out of Halley’s visit to the island of St Helena in the south Atlantic Ocean in 1676 to observe the southern sky. He presented his results to the Royal Society in London on his return in 1678 and the following year published his catalogue of southern stars, Catalogus Stellarum Australium, with an accompanying map, both of which included the new constellation. The veteran Polish astronomer Johannes Hevelius, a friend of Halley, was the first to adopt the new figure when he showed the royal oak on his chart of Argo in his atlas Firmamentum Sobiescianum published in 1690.
Halley’s own chart, incidentally, depicted Argo as an English merchant ship flying a red ensign from the stern and the Cross of St George from its topmast, doubtless in tribute to the East India Company whose ships had transported Halley to and from St Helena.
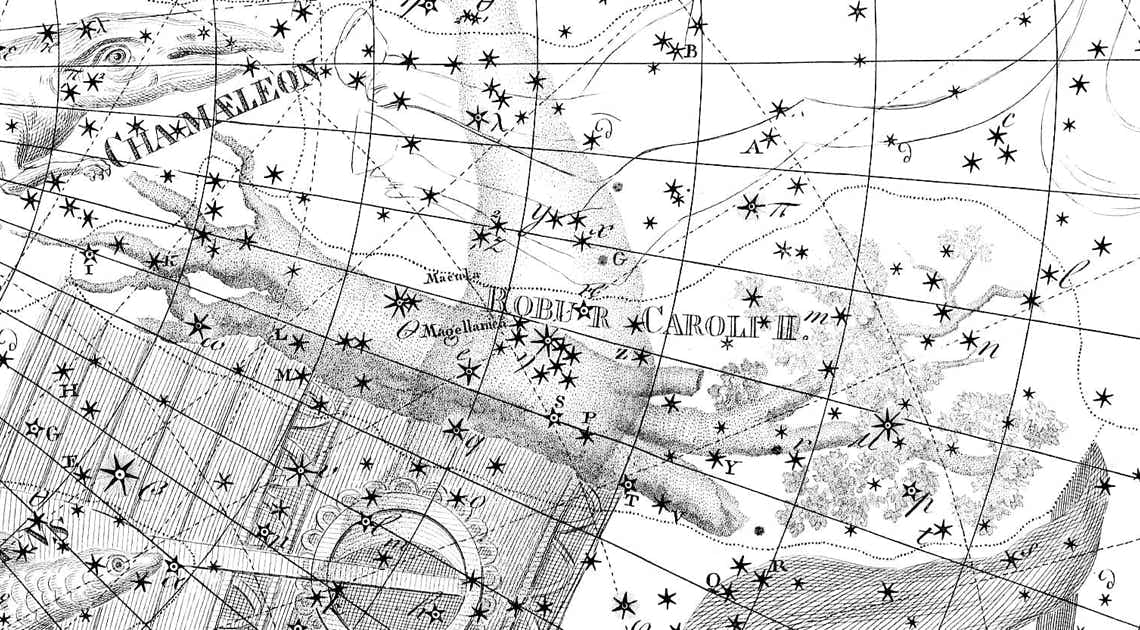
Robur Carolinum shown under the name Robur Caroli II on Chart XX of the Uranographia of Johann Bode (1801). It was positioned where the hull of Argo Navis (bottom of picture) was cut off, a place occupied on other maps by either the Clashing Rocks or clouds.
Click here for Halley’s original depiction on his own chart.
Halley listed 12 stars in Robur Carolinum. The brightest of them, in the tree’s roots, was the second-magnitude star we now know as Beta Carinae, a later designation assigned by Nicolas Louis de Lacaille. The fourth star in Halley’s list, placed among the branches, was the peculiar eruptive variable now known as Eta Carinae, another Lacaille designation; Halley’s catalogue was the first record of it.
Halley described his new constellation as being a ‘perpetual memory’ of the King, but it turned out to be less permanent than either of them would have hoped. The royal oak was uprooted by the French astronomer Nicolas Louis de Lacaille who mapped the southern stars more comprehensively 75 years after Halley. Lacaille wrote that he disapproved of the way in which Halley had taken part of Argo to make the new figure, although doubtless he also disapproved of Halley’s nationalistic motives. Most astronomers followed suit in ignoring this genuflection to an English king, one notable exception being Johann Bode who included it on his Uranographia atlas of 1801 as Robur Caroli II (see illustration above). Even Bode’s support, though, could not prevent the tree’s eventual extinction.
© Ian Ridpath. All rights reserved
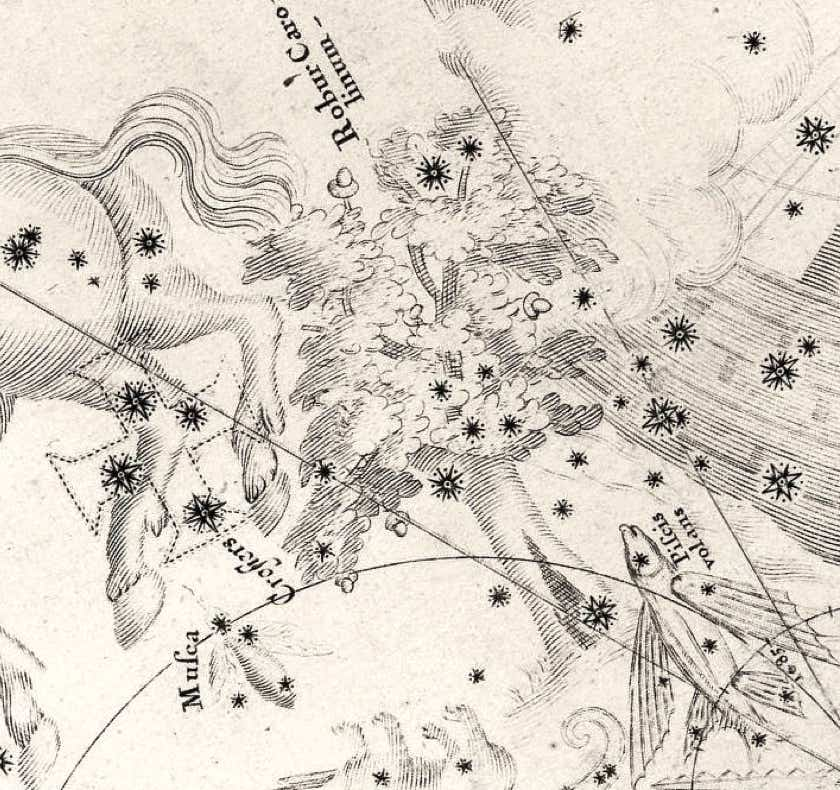
Halley’s depiction of the royal oak, Robur Carolinum, complete with acorns, on his southern star chart of 1678. To the left of it is the Southern Cross, and to the right the False Cross. At the base of the oak’s trunk is the present-day Beta Carinae. At the top of the trunk, just beneath the leaves, is Theta Carinae, the brightest member of the cluster IC 2602, popularly termed the Southern Pleiades. In the leaves above it is a group of four stars including the peculiar eruptive variable Eta Carinae. The extensive Carina Nebula that surrounds it, allied to the dense Milky Way starfields in this area, would have helped give the impression of foliage.
Edmond Halley dedicated his new constellation Robur Carolinum to King Charles II of England in his Catalogus Stellarum Australium of 1679.